AKKUDUK
Overview
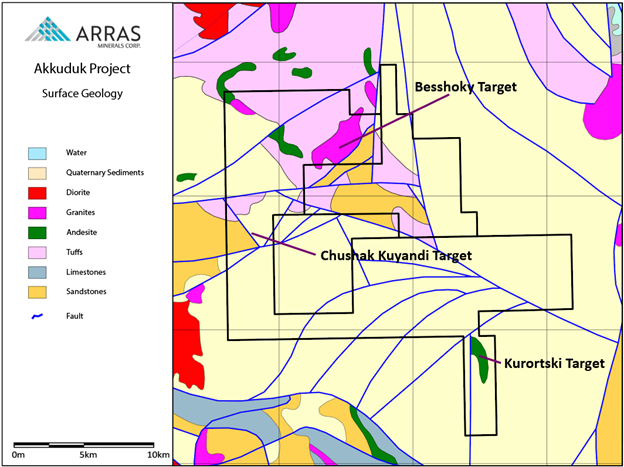
The Akkuduk project consists of two licenses covering 326.3km2, located project is located 103km to the southeast of Ekibastuz. The project is located adjacent to the Central Kazakhstan Fault, a major (>1000 km) trans-crustal fault.
Akkuduk summary geology map
Geology
The geology at Akkuduk consists of Devonian and Silurian-aged porphyritic andesites and basalts emplaced into tuffaceous sediments and conglomerates. Into which, several diorites and granodiorite intrusions have been emplaced.
Initial exploration by Arras have defined three principal exploration targets have been identified.
Besshoky
The Besshoky prospect consist of large (25km2), unexplored lithocap coincident with Soviet-era Cu-Au-Ag-Mo-soil anomalies and historic-IP chargeability anomalies.
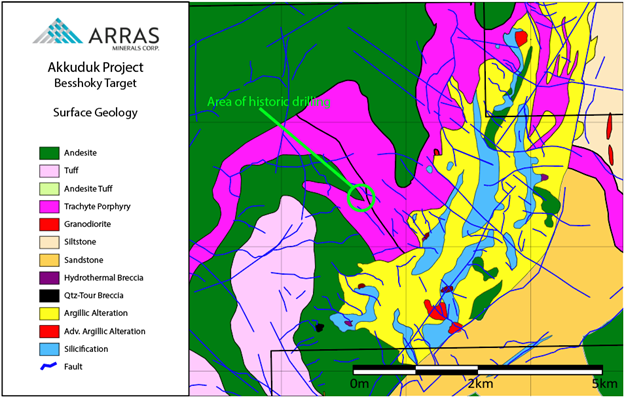
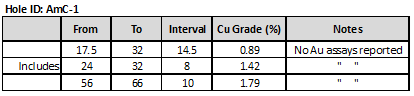
Historic drilling (2 holes, totalling 300m) adjacent to the Besshoky lithocap intersected disseminated chalcopyrite mineralization that returned:
Recent mapping by Arras has identified extensive hydrothermal alteration, explosion breccias with sulphides, wide-spread secondary quartzites and advanced argillic, phyllic and propylitic alteration, suggesting that the Besshoky target represents the high-level of a large porphyry-epithermal system.
Chushak Kuyandi
Porphyry-epithermal. Igneous complex (diorites, quartz diorites, diorite porphyry, and granodiorites) with propylitic, argillic and phyllic alteration reported and complex Cu-Mo-Pb-Zn soil anomalies. Trench samples up to 2% Cu and 10 g/t Au.
Kurortski
Geology dominated by a 15km long by 2.5km wide late Devonian intrusion (diorites, gabbros and monzodiorites) emplaced into Silurian sediments (siltstones, and sandstones). Gold mineralization occurs as a series of sheeted closely placed contiguous steeply dipping quartz-sulfide veins cutting quartz-chlorite-epidote-carbonate altered rocks.

